nezi starih
Čuvajte znanje i iskustvo koje dolazi sa tim.

situaciju
Najveća pohvala za nas krije se u osmehu našeg pacijenta.

bolji život
Verujemo da se njihov život može nastaviti i biti aktivan.
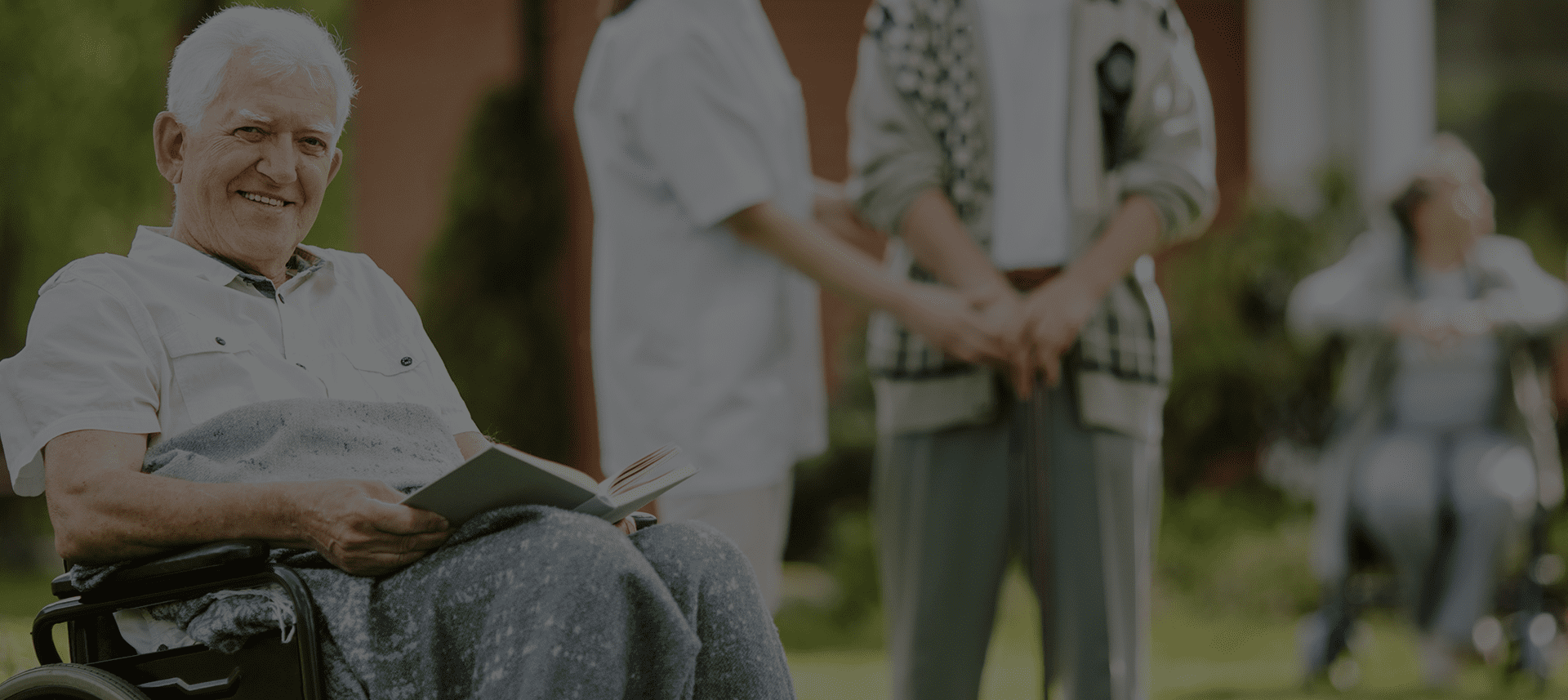
PROFESIONALNA NEGA KOJOJ MOŽETE DA VERUJETE
Niste sami
Uspeh našeg centra , ogleda se u broju zadovoljnih korisnika i njihovih porodica. Život je dar i u skladu sa tim naš cilj je da podržimo kompletnu osobu – um, srce i telo.
Svako životno doba, nosi sa sobom neke specifičnosti a na nama je da Vam pokažemo da možete da uživate u svakoj verziji sebe i uvek pronađete način da pomognete sebi ili svojim najbližima
MinuteNurse Organizacija – Centar za negu starih i bolesnih nametnuo se kao jedna od najiskusnijih kompanija za kućnu negu u industriji. Kreiramo inovativna rešenja koja poboljšavaju zdravlje i kvalitet života onih kojim su potrebne zdravstvene usluge u kući.
STRUČNA I KVALITETNA MEDICINSKA NEGA ZA VAŠE NAJBLIŽE
Za seniore i juniore
NEGA KAKVU ZASLUŽUJETE
Zašto baš mi?
-
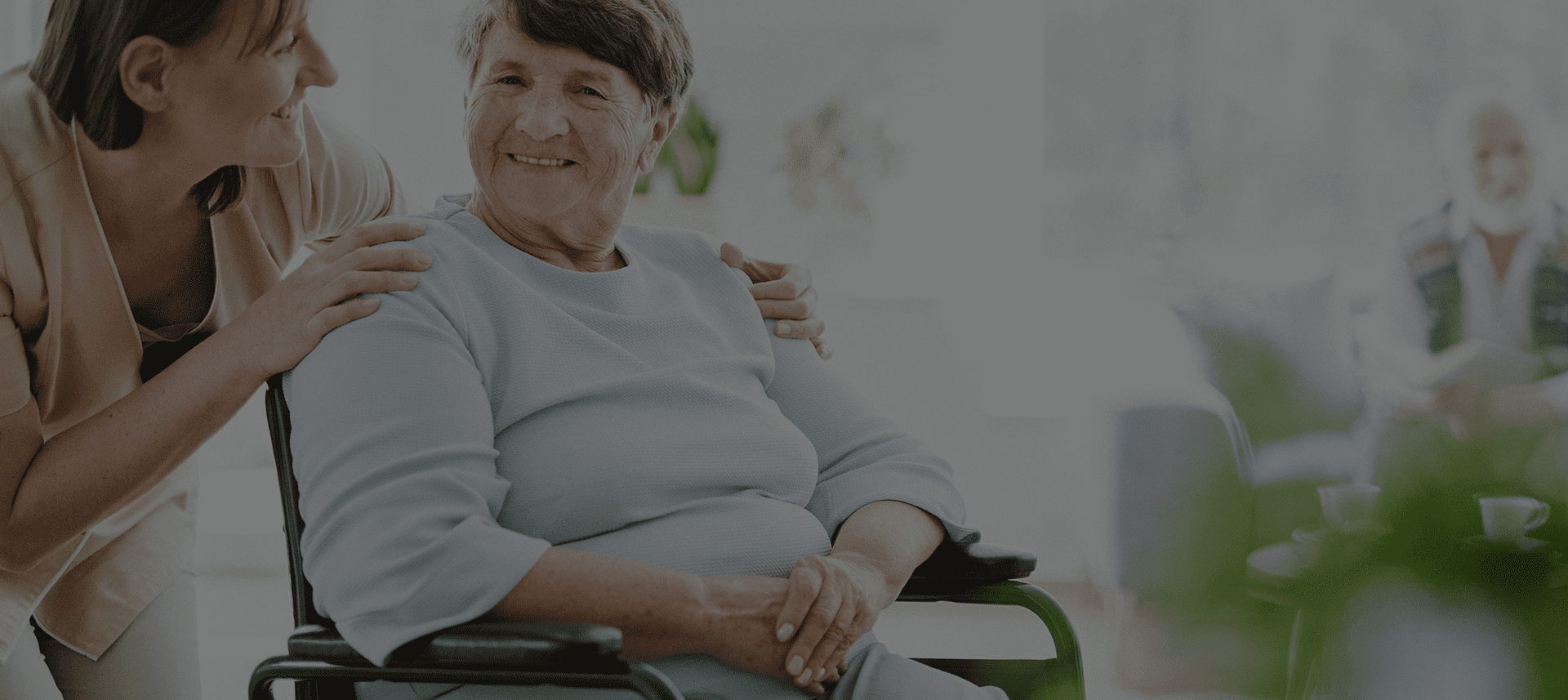
Ispunjavamo vaše emotivne potrebe
Starijim osobama je neophodno da osećaju sigurnost i pripadnost sa verom da se život nastavlja.
-
Negujemo vaše telo i brinemo o fizičkim potrebama
Nudimo stručne medicinske i negovateljske usluge našeg tima koji brine o očuvanju vitalnosti vašeg tela i pružanju nege koja Vam je potrebna.
-
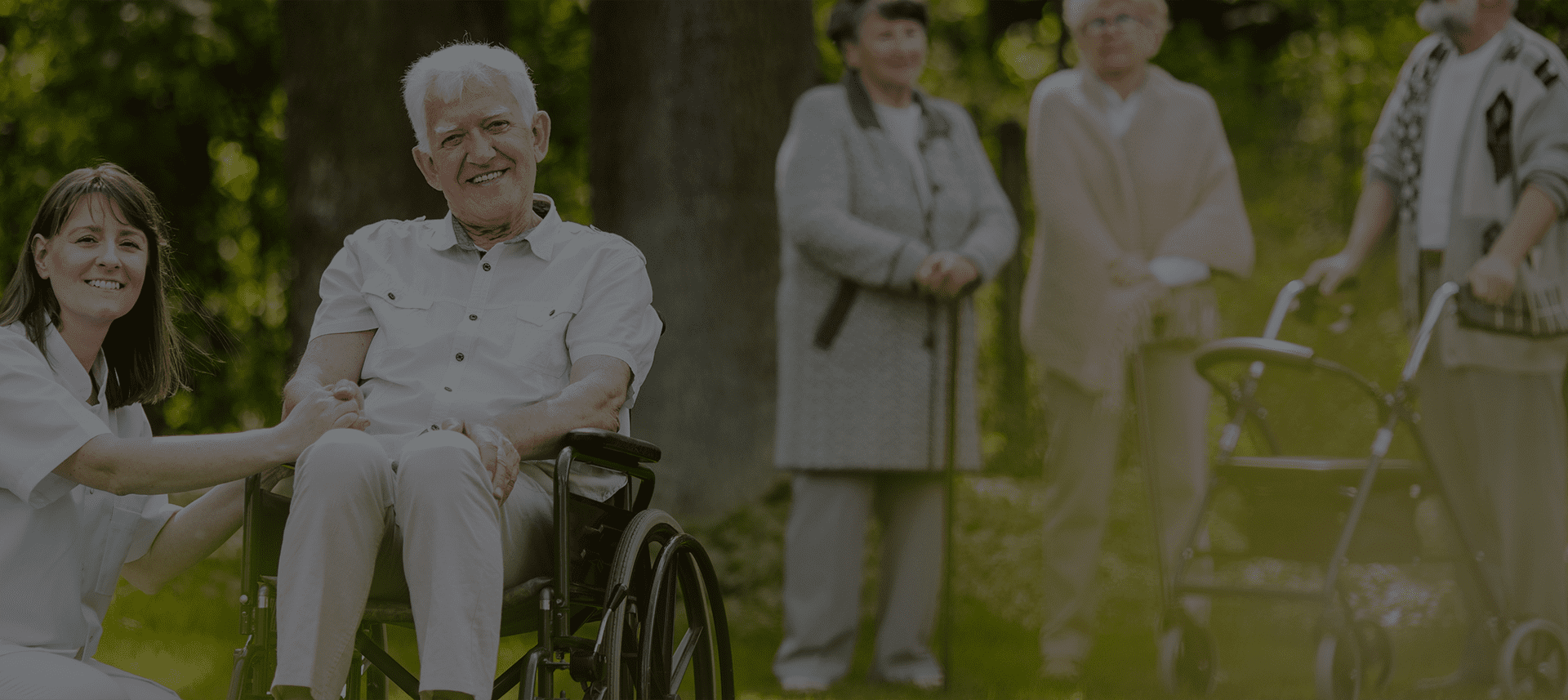
Trudimo se da ostanete nezavisni
Pomažemo našim starijim korisnicima da očuvaju integritet, samopuzdanje i mogućnost da žive samostalno.
Naš tim
Ko smo mi?
Sloba Dželebdžić
Dr Saša Dželebdžić
Dr Đurđa Filipović
Danijela Branković
Miljana Stanojević
Milica Dželebdžić
SAČUVAJTE SLOBODU I NEZAVISNI ŽIVOT - ZA PAROVE
O Minute Nurse Home Care centru
Brinemo o Vama i vašim najmilijima s ljubavlju
“Brinemo o Vama i vašim najmilijima s ljubavlju”
MinutNurse Home health & care – Centar za negu starih i bolesnih nametnuo se kao jedna od najiskusnijih kompanija za kućnu negu u industriji.
Više od 20 godina kreiramo inovativna rešenja koja poboljšavaju zdravlje i kvalitet života onih kojim su potrebne zdravstvene usluge u kući.
Naša pažnja prema kvalitetnoj nezi usresređena je na posvećenost pružanja nivoa stručnosti, obuke, usluge pacijentima i praćenje koje je teško podudariti u našoj industriji.
“Briga za starije posao je ljubavi i zahteva posebnu osobu”
Sve što radimo u životu vođeno je našom univerzalnom misijom da poboljšamo život u nezi. Mesto koje zovemo dom je mesto koje se oseća najudobnije i najsigurnije.
Osećaj za dom može postati posebno važan kako starimo. Naše usluge nege starih u kući pomažu u ublažavanju izazova starenja, dok podstiču starije osobe da uživaju u udobnosti svoga doma.
“Brinemo o Vama i Vašim najmilijima sa ljubavlju”
Uz stručno osoblje i kvalitetne usluge, trudimo se da poboljšamo kvalitet života korisnika, pomognemo im da očuvaju dostojnastvo i održe odnose sa svojim porodicama.
MinuteNurse Senior Care Center nudi pristupačne usluge nege u kući 24 sata dnevno, 365 dana u godini za one kojima je to potrebno.
Zakažite razgovor sa našim koordinatorom u našoj najbližoj lokalnoj kancelariji.
“Briga za starije posao je ljubavi i zahteva posebnu osobu”
Briga o starijim osobama ili jednostavno briga o starijima, predstavlja ispunjenje posebnih potreba i zahteva koji su jedinstveni za starije građane.
Ovaj širok pojam obuhvata usluge kao što su pomoć uz pomoć života.
Dnevna nega odraslih, dugotrajna nega, kućna nega, nega u domovima za stare.
Zbog široke lepeze brige o starijima koja se nalazi na nacionalnom nivou, kao i zbog razlikovanja regionalnih perspektiva o starijim građanima, ona se ne može ograničiti na bilo koju pojedinačnu praksu.
Šta drugi kažu o nama
Svedočenja
Kontaktirajte nas
Budimo u kontaktu
Naši partneri

Preporuke
Ambasada Kipra

Ambasada Pakistana

Pratite Nas
Dobijte uvide koji su vam potrebni da pružite svojim voljenima brigu koju zaslužuju